NGO registration is vital for any kind of organization. This allows a group to get permission for certain activities.
Several registered NGOs across India are working to eradicate discrimination against women, help save wildlife, and enhance education and awareness for the underprivileged.
Several registered NGOs across India are working to eradicate discrimination against women, help save wildlife, and enhance education and awareness for the underprivileged.
However, anyone can register an NGO in India without following any formal procedures. In general, there is no minimum membership requirement for the NGO. In addition, the minimum requirement for NGO registration is only some basic details, like the number of members and a website. NGOs in India cannot collect any funds from people outside the country unless they have a special certificate from the Income Tax Department.
How to Register an NGO In India?
There are many reasons why you should consider registering a new NGO in India. Not only will you be helping the country’s development efforts, but you’ll also be giving back to the community in a meaningful way. You can begin with just setting up a website and a Facebook page.
The next step would be to register it in India so that you can begin collecting funds from donors and foundations around the world.
There are two primary funding sources for non-governmental organizations (NGOs) in India. The first is government grants, which represent nearly 90% of NGO funding.
Government grants can fund various purposes, including hiring full-time staff positions, developing programs, covering travel expenses for staff members working abroad, and maintaining equipment.
The second source of funding for NGOs in India is individual contributions; such are, funding from other non-profits, the sale of services or goods, membership dues, private donations, and many other sources.
Before starting an NGO, you should involve yourself in some work, whether at an individual level or through a foundation. Registering as an NGO allows you to access funds from various agencies and funds that you can use for any purpose, including hiring employees or providing medical facilities at private hospitals or maternity homes, among other uses.
NGOs are an overlooked part of Indian society. Organizations such as Human Rights Activists, Students Human Rights Activists, Public Interest Organizations, etc. have been fighting for social and political rights for decades without getting any recognition from the Indian Government or the public. As one of the largest development agencies in India, International NGOs play a crucial role in making India a better place.
The online NGO registration process for an organization in India can seem overwhelming. There are many documents to submit, contradictory advice on what is the acceptable online expression, and questions on whether you should be paying by check or online EFT. There is no doubt that information security is a sensitive matter that you cannot take lightly. That is why we have sought out experts who have experience in handling such matters. To assist you, we have experts, with years of experience in handling NGO Registration processes in India.
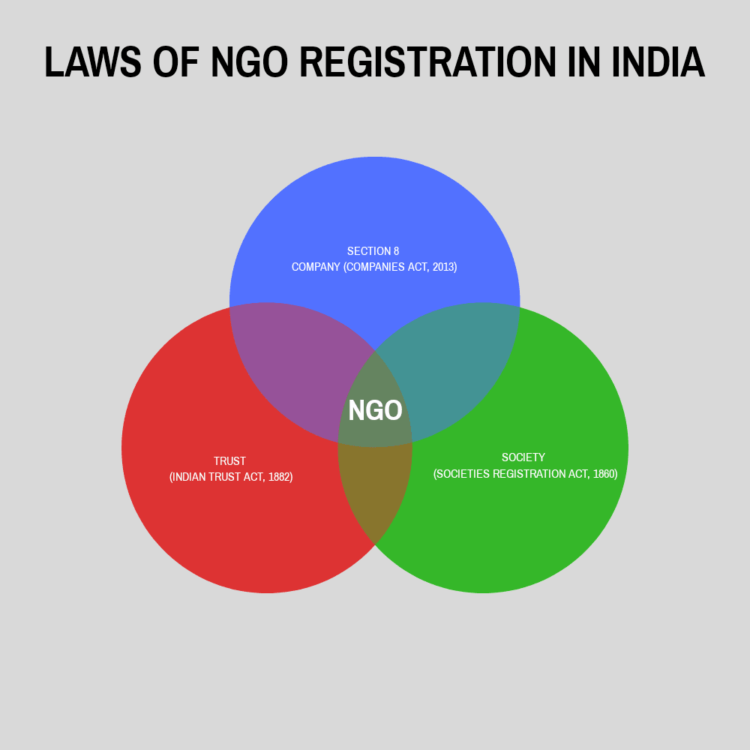
Various Types of NGO Registration in India and its benefits
There are around 3 major types of NGOs in India which are governed by different laws of NGO registration.
- Section 8 Company, Company Act, 2013
- Trust, Indian Trusts Act, 1882
- Society, Societies Registration Act, 1860
Trust and Societies have their laws and regulations that depend upon the state you are getting it registered. However, Section 8 Companies follow the Companies Act, of 2013.
For greater transparency on the administration and functioning of an organization, there are good reasons why you should opt for the NGO registration process. NGO Registration gives you many rights, besides the financial benefits that come with it.
In addition to having the authority to combat poverty and disease, organizations also enjoy the privilege of conducting opinion surveys, creating ad campaigns, registering disputes, and compiling information on budgets and finances. This helps you understand how your hard-working government functions.
Online NGO registration as “section (8) company”

Have you always wanted to use your talents for the benefit of others? If so, a Section 8 company is for you. These companies focus on promoting fields such as arts, commerce, science, research, education, sports, environment, and more. You can register as a Section 8 Company under the Company Act, 2013. These companies are registered either as a Private limited company(required 2 directors) or a Public Limited company(required 3 directors).
Under the Indian Companies Act, 2013, this type of company doesn’t need to include the words “Limited” or “Private Limited” in its name. Also, these companies are required to follow the same rules that apply to a Private Limited Company or Public Limited Company.
The Central Government can accept an application from a person or group of people to form a company with charitable objectives if the conditions are met. Once you’ve paid all the requisite fees, the Registrar of Companies will register your company.
You may be thinking about what conditions should meet the prospects of registering an NGO in India. That is nothing different than what you can assume when you register for a company in India. The conditions are like this; INC 29 form cannot be used for incorporating section 8 company when you do not intend to promote any of the science, for environmental good, social welfare protection, art, sport, research, etc.
Benefits of a Section 8 Company
A section 8 company is a form of society or association. A section 8 company offers a number of advantages to the members. An important point to note is that in the case of illegal businesses, you cannot offer a Section 8 company protection to the beneficial owners of the companies. However, in other cases, you can give the company a certificate of qualification by the authorities. Here are the benefits that will help and support you to grow and spread more care to needy people.
- The company can offer certain concessions in the taxation system, such as income tax.
- No stamp duty for the Section 8 company registration process.
- Not just an individual, but a firm (sole proprietorship, partnership, etc.) can be a member.
- Not required to use Pvt. LTD. extensions, however, this is optional.
- No share capital introduction is required.
- Limited liability protection.
- Various benefits from central government.
Documents required for Section 8 Company
The following documents are needed in order to register your company as Section 8:
- The utility bill of the office where you are operating your NGO from, the bill should not be older than 2 months.
- NOC / Rent agreement (if required)
- Details of all the directors, such as their directorship if they are active as a director in any other company.
- Passport-size photo of all the directors.
- Copy of anyone’s Driving License, Aadhar Card, Voter ID card, or Passport.
- Copy of PAN Card of all directors and shareholders.
Online NGO registration as “trust”

Under the Indian Trust Act of 1882, a trust is a legal instrument established with the purpose of having one party hold property on behalf of another. It involves a designated trustee who manages the property and distributes it to the beneficiary once the objective is achieved.
Trusts are classified into two types in India: private trusts and public trusts. Private trusts are governed by the Indian Trusts Act, of 1882. Meanwhile, Public trusts can be either charitable or religious in nature.
Several statutes enforce Indian public trusts, including the Charitable and Religious Trust Act of 1920, the Religious Endowments Act of 1863, the Bombay Public Trust Act of 1950, and the Charitable Endowments Act of 1890.
Public Trust
People create public trusts for charitable, community, or religious purposes. These trusts differ from private trusts, which can transfer wealth to beneficiaries and are intended solely for the benefit of the public.
Private Trust
The Indian Trust Act, of 1882 regulates private trusts. These trusts are formed for transferring wealth or benefits to the beneficiary or to your loved ones. You can also transfer your movable and immovable property to the trustee. A trustee is a person who holds property on behalf of someone else. That’s right, you guessed it, the beneficiary.
A trust is a legal arrangement that has three parties: Trustor, Trustee, and Beneficiary. The idea is that the Trustee will manage the assets of the Trustor and distribute them to the beneficiary.
Besides the major trust type, there are other other types of trust. You may find worth knowing about these:
Special Trust: Here, the trustee is an agent and fulfills Granter’s wishes. Granter is actually the person who created the trust.
Simple Trust: A Simple or bare trust is a type of trust in which the trustee does nothing but hold the property and pass it on to the beneficiary, as determined by the trust.
Express Trust: The Settlor establishes a Trust over his assets with either a will or a Trust deed. The Settlor can set it up to happen either in the present or upon the Settlor’s death.
Implied Trust: You don’t have to go through the legal requirements of an Express Trust, but this type of Trust is designed to be legally treated as one.
Benefits of Trust Registration
- Various tax exemptions from Income tax.
- Trusts provide help to those who are struggling and in poverty.
- Trusts are a way to own specific assets, like land or a family company, that might not be right for a settlor to divide between individuals. People or groups of people can use the trust to benefit from assets without wanting to own them.
- Trusts can use the Gov. registered name.
- 80G certificate
- Setting up a trust when you relocate to another country is an excellent way to protect your family’s wealth and provide flexibility in its organization. However, It requires detailed professional attention.
Documents Required for Trust Registration
The documents below are necessary for the registration of a Trust:
- Any Aadhar Card, Voter ID card, Passport, Driving License of Trustee and Trustor.
- Trustee and Settlor Pan Card.
- Passport size Photo of Trustee and Settlor.
-
The person doing the registration should arrange the trust deed during registration.
- Occupation information and self-attested copy of ID and Address proof.
- Trust objective.
- NOC or Rental Agreement if the trust property is on rent.
- Address proof, such as Telephone bill, and electric bill (not older than 2 months).
- The name of the trust.
-
During the registration, two witnesses and a settlor must be physically present.
- The number of trustees.
- Rules and regulations of the trust.
Online NGO registration as “society”
Society is a group of people who unite in order to accomplish a common purpose.
The Society Registration Act of 1860 reflects this. When you register, your society will become legal as an NGO and it will be easier to work with one another for activities like fine art performance, literature, knowledge, scientific, charitable or literary works, etc.
Society Registration is a law that enables society to get a legal status in India. It also improves society in terms of its legal conditions.
Benefits of Society Registration
There are various advantages of society registration in India:
-
Societies have the status of a legal entity.
-
Even if the membership changes, society remains a separate legal entity.
- A society can buy, lease, rent, sell or buy, borrow money, or participate in contracts, a property on its name.
- Members do not have the right to own an asset.
- It gives eligibility to open separate bank accounts for society.
- Members are responsible for any unlawful activities and obligations done by them.
- Income tax benefits as like any other NGO legal entity.
Documents required for Society Registration
Here is the list of documents required for registering a society in India:
- List of the members.
- All the member’s residential proof such as driver’s license, any utility bill (not older than 2 months), Passport, etc.
-
The person who is assisting you with society registration will prepare the Memorandum of Association.
- Society’s rules and regulations details.
- The objective of the society is in the form of covering later.
- Society’s registered address proof (Any utility bill not older than 2 months)
- NOC or Rental Agreement if the society property is on rent.




